In this blog MA Curating Collections and Heritage Renee Keeffe describes her current work placement with the World Cultures team at Brighton & Hove Museums. She originally presented her insights at a public event organised by the university’s School of Humanities and Social Sciences which celebrated the many collaborations the university has with local and regional partners.
My name is Renee. I am currently pursuing my Master’s degree in Curating, Collections and Heritage. I am excited to share with you a wonderful opportunity I had to do for my professional placement at the Brighton & Hove Museum. I am a big advocate for the professional placement model on the course.Currently, my placement involves working with the ‘World Art team’, which consists of Portia Tremlett, the head curator, and Sandra Bauza, the assistant curator. My particular interest is Indigenous material culture and heritage. The following images give a sense of the work that I’ve been doing.
I walked into the office, which was one of the first exciting moments, viewing the museum’s own research library in their large bookshelves.
What did I get out the Placement?
I’ve been involved in various tasks at the museum, such as understanding how cataloguing works…..
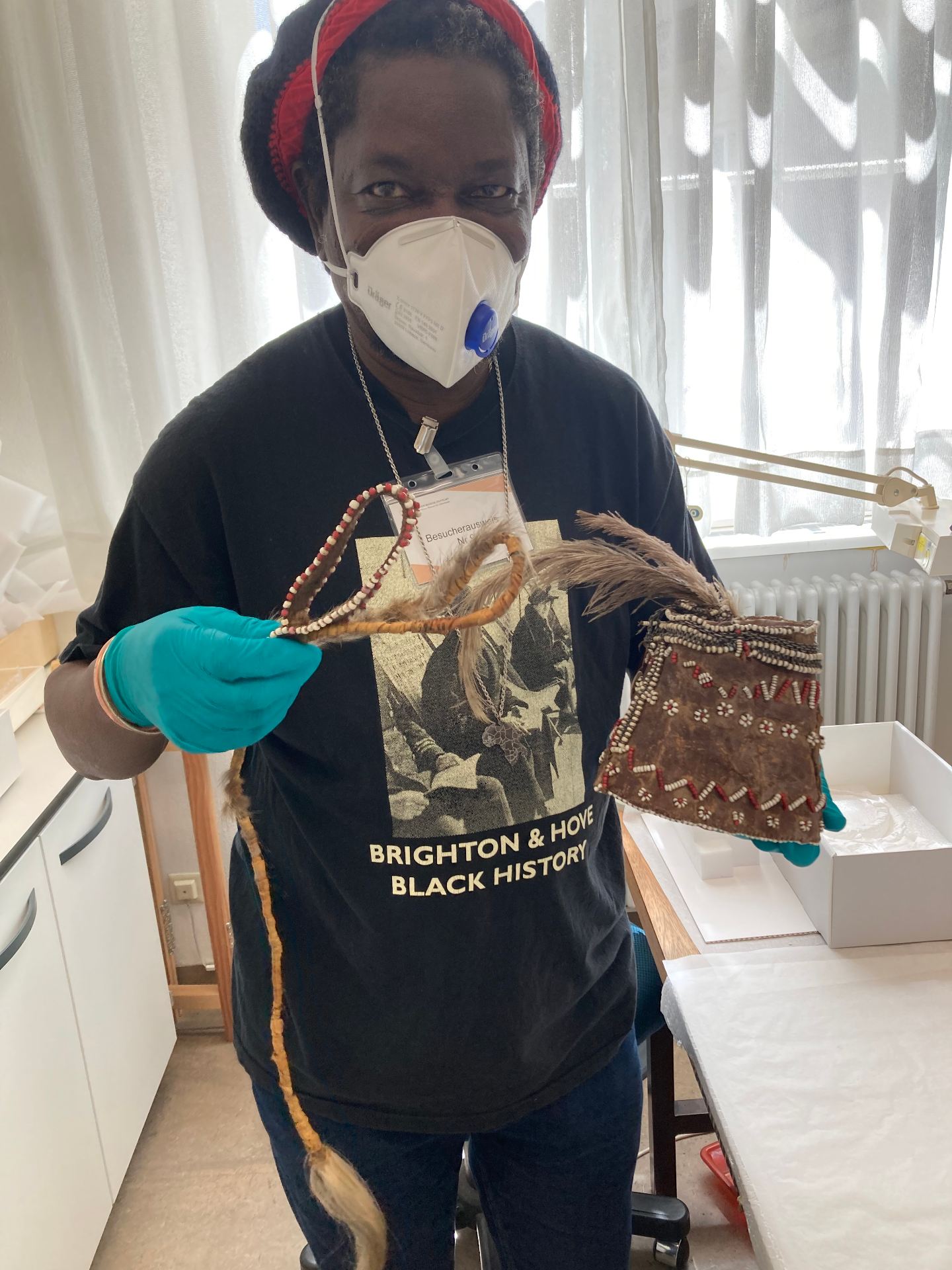
The process of cataloguing gave me a practical experience of working with the museum’s collections and object handling right through to learning how objects are created or acquired into the museum. I focused on understanding documentation procedures such as examining documents and filing the them on the museums systems.
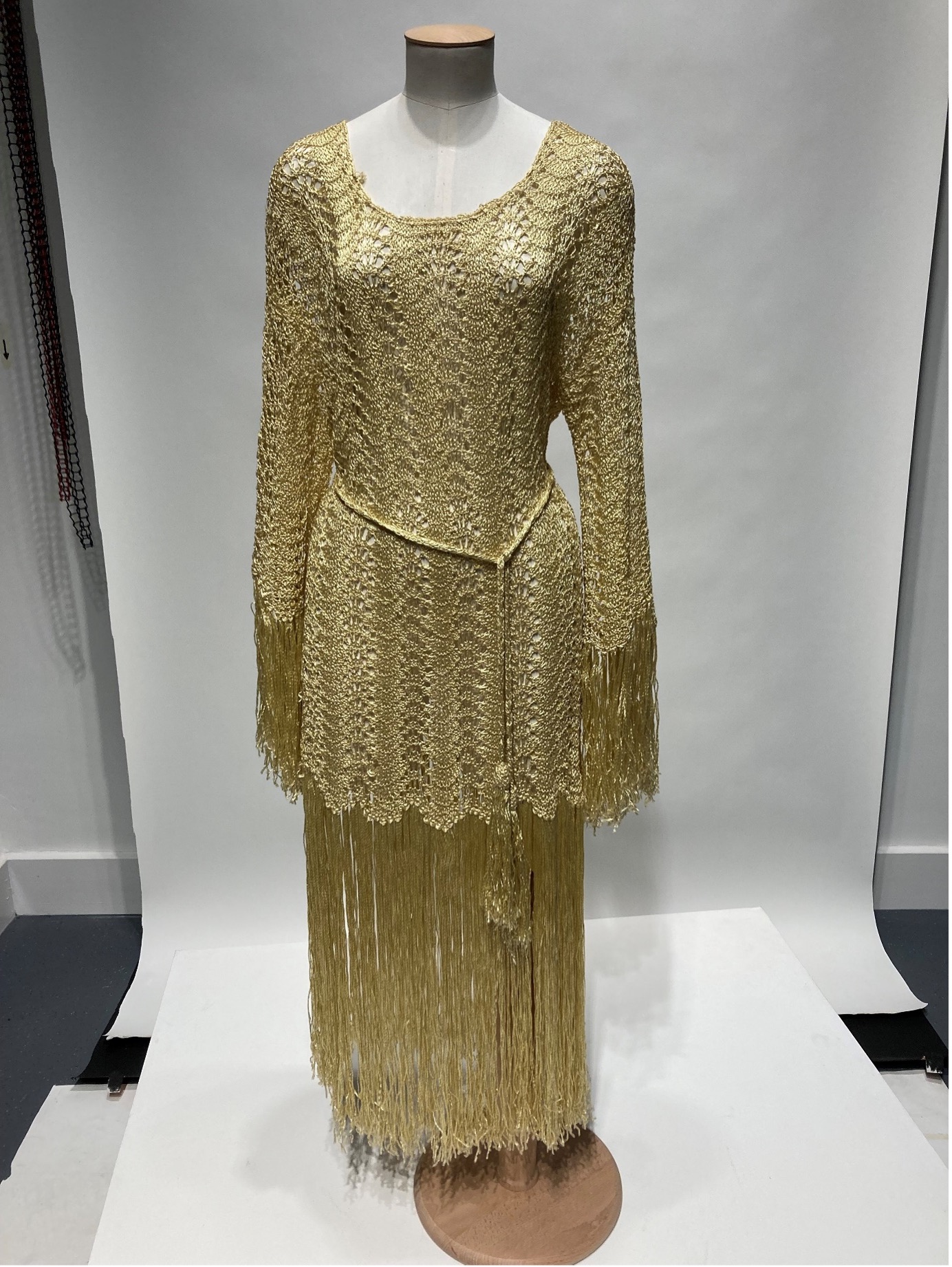
Collections: I learned where artefacts or objects are kept or stored, and how they were filed through the museum’s collections management system called Mimsy. I learnt how objects were collected, or who collected them, and learnt to describe the objects in the sytem.
Loans: I’ve also gained experience while working with loans from the British Museum, ensuring that the objects come back correctly with all the necessary checks on the garments and paperwork.
Research: during my placement, a research team called the ‘Oriental Raids Textile Society’ in London also researched Burmese textiles. They examine each garment closely and observed how each garment’s design and weave revealed its particular provenance.
Digital Archiving: I also learnt how digitization is incorporated into the collection management system through mimsy and excel in order to share information with other researchers.
Throughout my professional placement at the Brighton & Hove Museum, I’ve developed several transferable skills that are valuable in both my current field and potentially in others. The diverse range of tasks I did, which has significantly contributed to my personal and professional growth.
Here are some of the key transferrable skills:
Strong Communication Skills: Working closely with museum staff, from curators to assistants, has improved my ability to communicate effectively. Whether discussing the specifics of loans from other institutions or engaging with digitization processes, clear and effective communication has been crucial.
Teamwork: My experience at the museum underscored the importance of collaboration. Engaging with different departments and learning from experienced professionals has taught me the value of teamwork in achieving common goals.
Multitasking: Handling various tasks simultaneously, from documentation procedures to object handling and cataloguing, has improved my ability to multitask efficiently while maintaining a high standard of work.
Ethical awareness/ cultural sensitivity/Cultural awareness
Critical Thinking/Problem Solving: Throughout my placement, I’ve encountered challenges that required innovative solutions. Whether it was regarding the safe storage of artefacts or navigating the museum’s database systems, critical thinking has been key to overcoming these obstacles.
Writing: Documenting acquisitions, loans, and object histories has enhanced my writing skills, making it easier to articulate complex ideas clearly and concisely, a vital skill in almost any profession.
Engagement: Actively engaging with staff and participating in museum activities has taught me the importance of being a proactive team member.
Commitment: Demonstrating dedication through consistent effort and a willingness to take on various tasks has been a crucial part of my placement.
Optimism: Facing challenges with a positive outlook has not only helped me through difficult tasks but has also contributed to a positive work environment.
Passionate: My passion for curating collections and heritage, especially relating to world cultures and indigenous material culture, has grown.
These skills, acquired and refined during my time at the Brighton & Hove Museum, are not only valuable in the context of curatorial work as well as archives and collections but are also highly transferable to a range of other professions and endeavours.
Next Steps
Drawing on the lessons learned during my placement, I am keen to foster greater connections between museums and indigenous communities.
My aim is to contribute to practical solutions that bridge cultural gaps possible by leveraging digital resources to preserve and share indigenous stories and knowledge on a wider scale with the archives and the collections. This means not just consulting on the representation of cultural objects in archives or collections but collaborating actively to ensure museums act as spaces of learning and respect for all cultures. This ethical approach aligns perfectly with my own research for my dissertation, particularly addressing complex issues such as decolonization and post-colonialism. Through continued learning and collaboration, I look forward to contributing to a future where museums play a central role in celebrating and preserving objects and their narratives of world cultures, especially those whose histories they hold.