Student pharmacists will be able to test their treatment skills on three new ‘sim people’ following a reorganisation of teaching space.
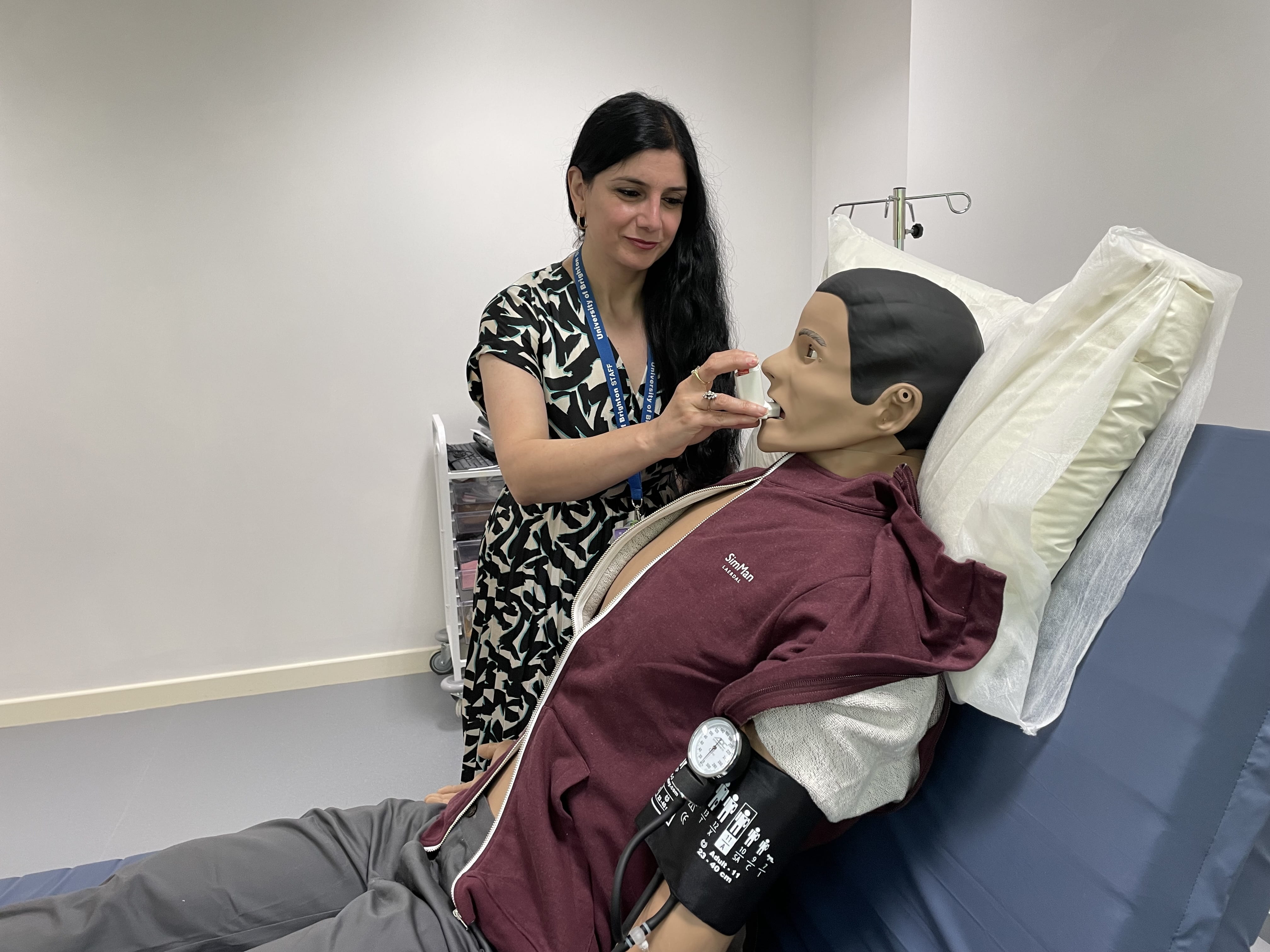
The idea is to hone students’ communication skills and decision-making when faced with patients in a variety of challenging scenarios. By ‘treating’ the mannequins for medical conditions such as anaphylactic shock, taking a blood pressure or responding to unspecified pain, our student pharmacists can build confidence before clinical placements.
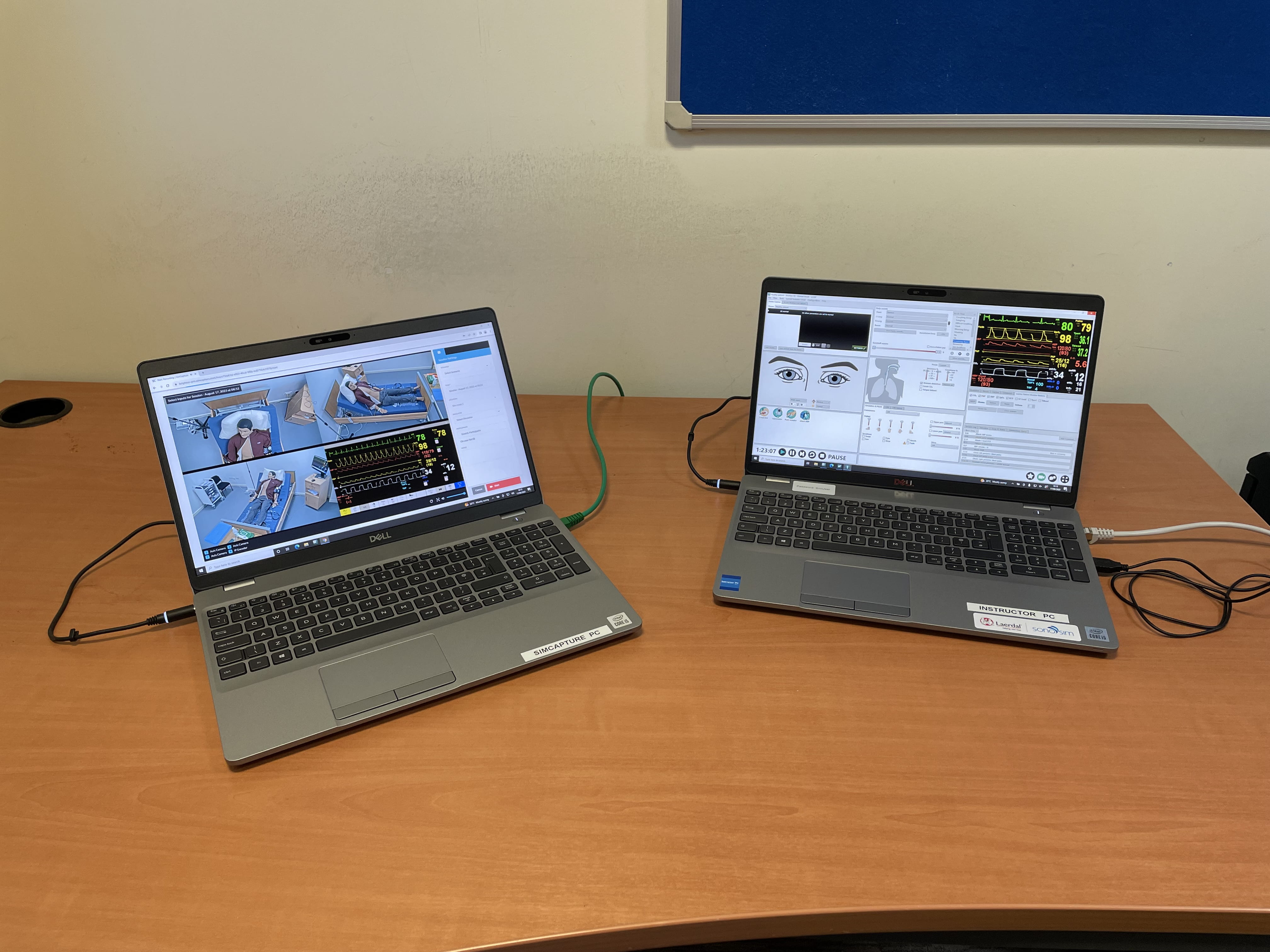
Lecturers don’t even have to be in the room to see how students are performing – they can keep tabs on what’s going on from a separate centre of operations via a live video link. As well as responding realistically to different medications, the mannequins also include a hidden microphone, which will allow lecturers to ‘speak’ on their behalf and respond in real time to what students are doing.
Jenny Minto, Principal Technician in the School of Applied Sciences, has been helping to set up the mannequins. She said: “In the past, students have had to work in quite large groups and haven’t had much hands-on experience, but now they can all have a turn as opposed to watching everybody else. When we get them in small groups, they can really have a go rather than feel embarrassed about getting it wrong in front of their peers.”
The student pharmacists will also be able to practise what it would be like to call other healthcare professionals – for example, to request a consult – via a telephone link from the treatment rooms to the lecturers’ centre of operations.
Hands-on experience
The mannequins were purchased two years ago from Laerdal but the reorganisation of teaching space in Huxley building on Moulsecoomb campus means that they can now be used to their full potential. The fully articulated dummies can be posed in a number of ways and the hope is to have them in a variety of situations – lying down on a hospital bed hooked up to a heart monitor, for example, or sitting up in a facsimile of a GP’s consulting room.
In line with other Inclusive Practice work being done in the School of Applied Sciences, the mannequins were chosen with diversity in mind, with dark hair and skin. They also come with interchangeable genitals and detachable breasts, meaning that student pharmacists can practise treating patients of different sexes – for example, examining the model breasts for lumps to rule out breast cancer.
Dr Melanie Flint, Reader in Cancer Research and the leader of a stress and breast cancer programme at the University, is excited by the possibilities. “I teach the breast cancer case for Pharmacy,” she said. “In our workshops we take students from diagnosis to living with cancer, as part of which an advanced clinical care nurse will come in and show them how to palpate breast tissue. That’s very important for Pharmacy students, with one in seven women being diagnosed with breast cancer in their lifetime. Although Pharmacy students don’t currently perform breast exams, they do get people coming into the clinic with suspected lumps so they need to learn about that.”
Having the mannequins will be invaluable, she believes, not just to give a physical demonstration but as a way of helping students to practise talking to patients. “The most important part is the communication,” she said. “Even if you have somebody who’s newly diagnosed who comes into the pharmacy clinic, if you’ve got a pharmacist who knows about this and can show empathy, they’re the skill sets we want to get from our workshops.”
According to Dr Matt Ingram, Associate Dean (Academic Operations) in the School of Applied Sciences and Principal Lecturer in Pharmaceutical Sciences, the new facilities have the potential to supplement students’ learning in other ways too. “The idea is that, in addition to their usual lectures, the students will be able to book one of the rooms to come in and practise, subject to availability,” he said.
“Thanks to the video links, one lecturer can see what’s going on in multiple different rooms simultaneously – and it can be streamed over Teams so our clinical team can observe when they are off site. There is also a facility to record to the cloud as well as livestream. These systems are fully compliant with General Data Projection Regulations (GDPR). Under supervision, students may be able to watch back and assess their performance later.”




Published by