What is Augmented Reality?
Abari, Bharadia, Duffield, & Katabi (2017) define augmented reality (AR) as the “interactive computer simulation which transfers sensory information to a user who perceives it as substituted or augmented.” However, I prefer LaValle’s (2017) definition which defines AR as “the action to induce a targeted behavior in an organism by using artificial sensory stimulation, while the organism has little or no awareness of the interference” LaValle’s definition gives essential aspect of AR being a technology that merges with real world to create what appears to the user as seamless as the picture below shows.
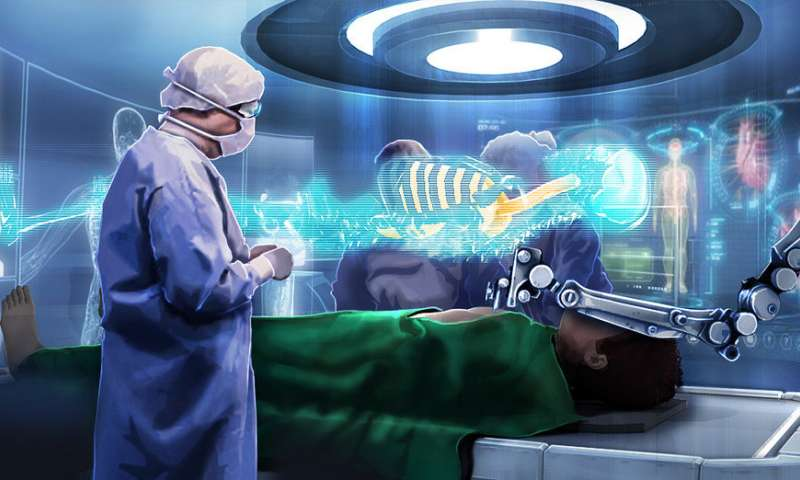
Augmented Reality enables more accurate biopsy Photo Credit: University of Twente
Augmented Reality Uses In Industry
Sarah Downey discusses the uses of AR in various industries.
Is Holographic Augmented Reality The Next Step to AR?
RealView Imaging delivers real-time 3D interference-based holograms
While the idea of Holographic augmented reality above seems exciting, the start-up costs for users are high. There is also an issue with scalability. Aside from the one app where else can users apply the technology? If developers are to make a success of this technology they need to extend usage from one app to a myriad of uses. This is the reason why I am in favour of the development of AR for mobiles because the start-up costs are minimal.
Risks of AR Apps
Platform Integration – which platform do VR apps use? It is important to design VR apps for the most widely used platforms. When it comes to AR most companies are designing their AR apps within their own platforms in-house eg Google Glass. The problem with this is that their AR apps will only work on their own devices or platforms. There is a need for standardisation in the AR industry, for example, the HTML5 standard is the same in every country, language or device. Apart from standardisation, collaboration in building platforms and apps that make efficient use of VR is also important. Collaboration would cut down on costs an development time.
Investment in development – Because AR is being developed by individual companies that have a fiduciary responsibility to shareholders, they are not likely to experiment in a technology where they have a high probability of crashing and burning. AR is still in its infancy and there is yet an unproven profit to be made. Risk-averse shareholders and managers are not likely to spend large sums on a product that does not have a high chance of financial return.
Privacy concerns – While users want to enjoy apps there is a delicate balance that app developers need to balance user enjoyment with user privacy. The VR app, PokemonGO on iOs made by Niantic received huge backlash in 2016 over its privacy settings which required full access to a user’s Google Account. Why did they need that kind of access for a game? It turns out their app didn’t need all that private information at all to function efficiently (Etherington, 2016).
How to do Augmented Reality Apps Well
Object Scaling in design – During the design phase, AR objects must be created in a manner that merges with the natural environment in terms of size to create a realistic feel for the user. It would appear strange if say a puppy in AR was the size of an 18wheeler truck.
Pre-Define Metrics or KPIs – During the origination phase, it is important to understand what the AR app will do for the user as well as what it will give the design company or app owners. There needs to be an in-built facility to track, analyse and optimise app performance. How else will a company know that its AR app is doing well? The following metrics should be taken into consideration:
- Downloads – How many downloads have been completed in the App store? This information is available to developers on major platforms like iOs, PlayStore
- Spread – What is the geographical and demographic spread of app usage? There may need to be more specific targeting needed in different locales and demographics.
- Reviews & Mentions – What are users saying about the app? What changes do users want to see? The sentiment analysis feature from Brandwatch would be useful to gauge how users really feel about the app.
- Open frequency – How many times a day/week is the app opened? This can help developers and marketers know if their offering is engaging enough.
- Time in-app – How long on average, do users spend interacting with the app? if it is a long time then check if the information is readily available?
- Value Creation – How does the App create value for both the company and the users? What keeps users coming back. Through Sentiment analysis mentioned above, study how users’ tastes, needs, and beliefs are evolving to keep your app relevant.
- Conversion Metrics – these analytics help you quantify if you are achieving your sales goals from your app. They also show you when your customers are likely to buy so you can better focus and optimise your app towards this.
Mobile cloud computing – As mobile devices have average computational power, small batteries as well as inherent rigidity in hardware and software development, there is the need for resource-intensive VR apps to use location-independent computing (Cloud Computing). This allows the “resource intensive tasks and all the complex functions to be performed in the cloud rather than on mobile and having the end results sent to the device and displayed in the screen.”
Usability Testing – before being rolled out to the general public, AR apps must for conform to rigorous user testing on a myriad of platforms and devices to ensure uniformity. Albertazzi et al advise that usability tests should include “knowing and defining the test objectives, the research questions, the participants’ characteristics, the methods, the task, the environment, equipments and logistics, the moderation rules, the gathering and evaluation of data and the results presentation.”
Branding consistency – An important aspect of app design is to maintain brand consistency in an app.
Social Commerce – If your app is an eCommerce app then the ability to share information as well as to collaborate on purchases is important. It is no secret that human beings are social creatures with an inane desire to gain approval from the ingroup.
References
AR In Action (2017). The massive list of AR use cases | Sarah Downey | AR in Action.
Available at: https://youtu.be/JrZsmfA56Sw [Accessed 1 Apr. 2018].
Etherington, D. (2016). Pokémon Go updated to address privacy concerns. [online] TechCrunch. Available at: https://techcrunch.com/2016/07/12/pokemon-go-update-addresses-privacy-concerns/ [Accessed 2 Apr. 2018].
Fernandez, M. (2017). Augmented-Virtual Reality: How to improve education systems. Higher Learning Research Communications, [online] 7(1), p.1. Available at: https://files.eric.ed.gov/fulltext/EJ1150087.pdf [Accessed 21 Mar. 2018].
Haptical (2018). Augmented Reality enables more accurate biopsy – Haptical. [online] Haptical. Available at: https://haptic.al/augmented-reality-enables-more-accurate-biopsy-cdb10a8f8a26 [Accessed 8 Apr. 2018].
Holzer, A. and Ondrus, J. (2009). Trends in Mobile Application Development. 1st ed. [ebook] Dorigny, Switzerland: University of Lausanne, pp.1-10. Available at: http://www.janondrus.com/wp-content/uploads/2015/08/2009-Holzer-BMMP.pdf [Accessed 1 Apr. 2018].
Intel (2012). Building a Mobile Application Development Framework. [online] Intel.com. Available at: https://www.intel.com/content/dam/www/public/us/en/documents/best-practices/mobile-app-development-framework.pdf [Accessed 28 Mar. 2018].
Kumara, A. (2017). Mobile Cloud Computing for Big Data Management in Future Smart Phone App Development. SSRN Electronic Journal, [online] pp.1-4. Available at: https://papers.ssrn.com/sol3/papers.cfm?abstract_id=2932652 [Accessed 27 Mar. 2018].
LaValle, S. (2017). Virtual Reality. 1st ed. Illinois: Cambridge University Press, pp.1-22, 331-380.
Martins, V., Soares, L., Mattos, V., Makihara, E., Pinto, R. and Guimaraes, M. (2012). Usability Metrics for Augmented Reality Applications. 2012 XXXVIII Conferencia Latinoamericana En Informatica (CLEI), [online] 41(41), pp.1-5. Available at: http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/6427125/ [Accessed 1 Apr. 2018].
NHS Innovations South East (2014). App Development: An NHS Guide for Developing Mobile Healthcare Applications. [online] Innovationssoutheast.nhs.uk. Available at: https://innovationssoutheast.nhs.uk/files/4214/0075/4193/98533_NHS_INN_AppDevRoad.pdf [Accessed 24 Mar. 2018].
RealView Imaging (2016). Holographic Augmented Reality – The Fundamental Advantages of Digital Light Shaping™ Technology.
Available at: https://youtu.be/cR-DxkBuZOk [Accessed 1 Apr. 2018].
