If your tablet sector company is using Facebook then you may struggle to cope with the constant demands of instant interaction, semantic analysis could help you to respond quickly and efficiently
“The World Wide Web is the single largest and most diverse repository of codified knowledge in the history of the human race” Shiri, M (2015). In 2014 it was found that roughly 40% of the world’s population was active on the internet (ITU, 2014)
With so much information available it can be daunting for organisations to unravel the meaning and relevance of it. Nonetheless, with suitable preparation the information can be transformed into a much simpler and understandable tool. Organisations use semantic analysis in order to gain insight into how their organisation is perceived, gain opinions and feedback. Semantic Analysis is an opportunity for organisations to be more active and go beyond mere public relations, they can use the tool to target customers to gain more attention and create a more narrow focus. You can build bonds with Facebook users, this reassures them that they have direct communication to the company.
Examples of Semantic Analysis on Facebook
Identified below is a comparison of the key players in the tablet industry, highlighting the use of semantic analysis technologies.
The first example of how an organisation could have used semantic analysis technologies is taken directly from the Kindle (2015) Facebook page, in March 2015 they were trying to raise awareness of national reading month. The company portrayed themselves positively, listing the comments by “most relevant”, the comments chosen were very encouraging and represented the company well, linking them with a good product.
Amazon Kindle
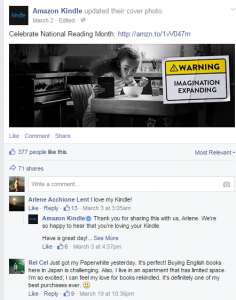
Figure 1: Amazon Kindle. (2015). Facebook page.
On closer inspection by clicking the “Recent Activity” option, other comments are obtainable which are less constructive. These comments were not listed as the most relevant and this is due to semantic analysis which would have chosen to show the flattering comments.
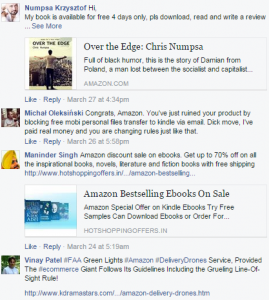 Figure 2: Amazon Kindle. (2015). Facebook page.
Figure 2: Amazon Kindle. (2015). Facebook page.
Organisations like Amazon know that users will probably skim read the relevant activity and are less likely to delve any deeper to view the unrelated comment. The impact of displaying relevant complimentary comments over irrelevant or negative comments is that it creates a better brand image. Users will be impressed by positive comments about the product and will therefore be more likely to purchase the product. Simple management of how the brand is portrayed can be highly influential over consumer perception.Semantic analysis technologies could have helped Amazon answer queries.
Panasonic
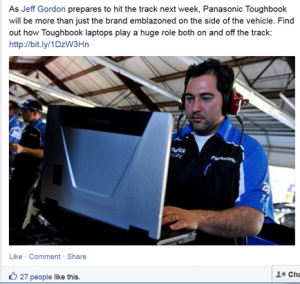
The like button is important as it allows organisations to target what their audience likes, and also related likes which may be useful in improving current strategies. An example of how the tablet industry could use the like button to their advantage is available on the Panasonic facebook page Facebook page.
Organisations like Panasonic can recognise which marketing strategies receive good responses and start to understand why. The semantic analysis technology will also allow Microsoft to view how their competitors are gaining a positive response from there public communication and therefore could implement a similar idea on their Facebook page. The share button is also significant as it gives an indication of a user’s opinions, sharing content means advertisements can reach users who haven’t liked the page.
Microsoft
Figure 4: Microsoft Surface. (2015). Facebook
Microsoft Surface. (2015) could use a time frame to measure how effective there affiliation with the well-known film ‘frozen’ has been. Semantic Analysis technologies allow organisations to change the overview of what they’re targeting at a specific time, an example of this would be to change date and time period that they’re analysing in order to identify how specific marketing movements had an impact.
How does semantic analysis work?
It’s possible for businesses to create a picture of the type of customer they serve. Users tend to display information about themselves on their profiles and this information can be retrieved with semantic analysis so that companies can target particular demographics. More specifically than this business can use Semantic Analysis technologies to identify similar interests and hobbies by checking what they have liked on Facebook or spoken about recently. The advertisements that would be aimed at this type of user is referred to as micro – targeted.
Mehra. M et al (2011) explains that semantic analysis technologies use ontologies, they’re important as they can be used deliver flexibility to the uses of Semantic Web. Using ‘Friend of a friend’ (FOAF) as an example, this ontology allows links to be made between social network sites and people by means of a ‘decentralised database’. The technology processes social network information such as Facebook likes, comments, shares and statuses.
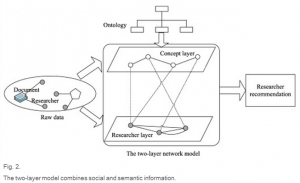
Figure 5: Mehra. M et al (2011)
Mehra. M et al (2011) introduces a two-layer network for researchers as shown in figure 5, in this model the circles in the ‘concept layer’ characterise knowledge of researchers in the arrangement of words or phrases. The connections in this stratum represent the semantic associations amongst research expertise areas. The circles in the ‘researcher layer’ represent researchers, and the associations amongst them characterise some types of social connections taking place, an example for this is Facebook conversations via comments. The associations concerning ‘concept’ and ‘researcher layer’ symbolise that a researcher illustrates know-how in the area.
Another ontology example is ‘Semantically Interlinked Online Communities’ (SIOC), this one permits the amalgamation of unrestricted online material such as blogs, forums, photos and so on. It can be more valuable when used as well as FOAF for outlining user summaries on social networks.
Veda Semantics is an example of an organisation which provides semantic analysis technology, although other outsourced companies are similarly effective. They state that there mission to
“Enabling businesses create better impact by uncovering actionable insights from unstructured data.” Veda Semantics. (2015).
They detail there activities further in the following video…
Veda Semantics. (2015).
Social media is a great way for organisations and consumers to interact, during these exchanges it is possible for organisations to collect data and use it to their advantage. The social network opportunity means that organisations no longer just view extracts of information, but also have the opportunity to engage with information. Semantic analysis is the process of mining information such user generated contents in order to categorise text. Sri, et al (2013) clarifies that opinion mining can focus on two types of opinion – ‘Regular opinion’s which just centres on ‘entities/features’ and ‘Comparative opinion’ which creates link and makes comparisons.
References
- Amazon Kindle. (2015). Facebook page. Available: https://www.facebook.com/kindle?fref=ts. Last accessed 27/04/15.
- ITU. (2014). ICT facts and figures. Available: http://www.itu.int/en/ITU-D/Statistics/Documents/facts/ICTFactsFigures2014-e.pdf. Last accessed 02/04/15.
- Michael Calaresu Ali Shiri , (2015),”Understanding Semantic Web: a conceptual model”, Library Review, Vol. 64 Iss 1/2 pp. 82 – 100
- Microsoft Surface. (2015). Facebook page. Available: https://www.facebook.com/SurfaceGB?brand_redir=427017100655129. Last accessed 27/04/15.
- Misha Mehra and Nishant Kumar (2011) Semantic Web Applications. Journal of Library & Information Technology, Vol. 31, No. 4, July 2011, pp. 217-225
- Panasonic. (2015). Facebook page. Available: https://www.facebook.com/ToughbookToughpad?fref=ts. Last accessed 27/04/15.
- Sri, S. and Devshriroy, D. (2013) Semantic Orientation of Sentiment Analysis on Social Media. International Journal of Computers & Technology, 10/2013, Volume 11, Issue 4 User
- Veda Semantics. (2014). Text Analytics and Social Media Monitoring from Veda Semantics . Available: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ijJCdxAIwW8. Last accessed 01/05/15.
- Veda Semantics. (2015). About Us. Available: http://www.vedasemantics.com/about-us.html. Last accessed 01/05/15.