
Belvedere Agricultural Park, Germany
The Belvedere Agricultural Park sits on the Western edge of Cologne. It completes the outer green belt of Cologne, which was initially conceived in 1917. The Belvedere Agricultural Park received public fund in 2010 in order to be realised, after being a part of the Regionale 2010.
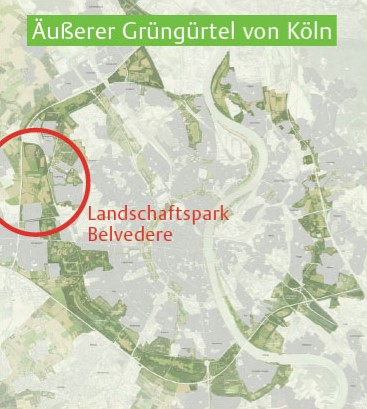
The Belvedere Agricultural Park completed the final part of the Cologne Green Chain. (Source: Office for Real Estate, 2022)
The Belvedere Agricultural Park approached the design of the park in an alternative way: ‘not to substitute agriculture in order to make a park, but to make use of it to create a new form of park’. Taking up an area of 300 hectares, the park operates as both a productive agricultural landscape and as an attraction for leisure and adventure. The park includes wooded areas, orchards, fields and viewing towers allowing people to view the landscape from above. Paths throughout the park have been created with a surface which allows for agricultural machinery, pedestrians, cyclists and skaters to use it. The system of pathways run alongside fields and through forested areas, making it quite attractive to anyone seeking relaxation in nature.

The park’s path system invites joggers, cyclists and other (source: Lohrberg Stadtlandschaftsarchitektur 2022)
Strips of wild flowers have been planted through the centres of the agricultural fields, creating habitats for pollinators, insects, birds and mammals. The flower strips will help reduce soil erosion and increase ecological diversity. They also contribute to a varied landscape, and when the flowers are in bloom, form colourful transitions between fields. The park provides habitat for over 40 species of birds including the endangered lapwing, skylarks and partridge’s. 20 square meter areas have been created in the park to protect the skylarks. These windows offer space for them to rest and rear their young.
The Max Planck Institute for Plant Breeding Research is situated in the centre of the park. It operates a teaching and show garden. The space highlights traditional species that have been cultivated in this area. The Vogelsang estate which sits next to it, cultivates the fields on behalf of the institute.

The Max Planck Institute for Plant Breeding Research has a show garden and educational space. (Source: Biennal Internacional de Paisatge Barcelona, 2022)
For further information see the Biennal Internacional de Paisatge Barcelona website.
https://www.arquitectes.cat/iframes/paisatge/fitxa/9851
Image: The park has four viewing platforms. (Source: Biennal Internacional de Paisatge Barcelona, 2022)
Back to previous page Related design projects
